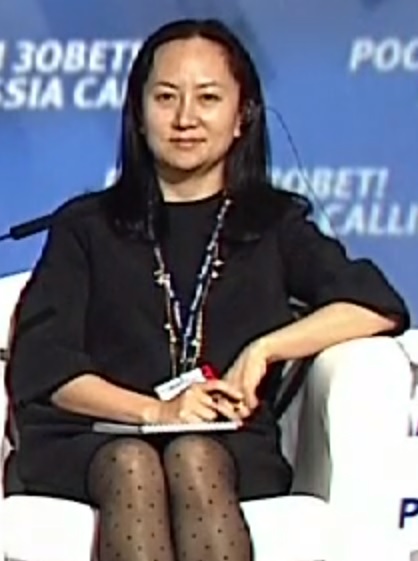
An executive of one of China’s largest tech companies is detained in Canada accused of violating US sanctions against Iran. This story has many threads, and each one reveals something very important about our world. In Part 1, I talk to activist and writer KJ Noh about the BC Supreme Court’s decision to keep Meng Wanzhou imprisoned in Canada.
Civilizations Series Episode 10: The American (Counter) Revolution
In world history, the American Revolution created a republic that continued slavery and expanded a continuous war against Indigenous nations in North America. We look at the British imperial geopolitics, the propaganda, and the history. Why wasn’t the American Revolution the inspiration that the French Revolution was? Special mention to two sources: John Grenier and Gerald Horne.
Civilizations Series Episode 9: Three Centuries of Power Politics (16th-18th)
From the Habsburg marriage alliances to the War of Spanish Succession, to the War of Jenkins’ Ear and the Seven Years War; to the Anarchy in India after Aurangzeb’s death and the founding of Afghanistan by Ahmad Shah Durrani. Some glimpses of three centuries of power politics in world history.
The Anti-Empire Project Episode 52: Reading Fanon with Stefan Kipfer
Stefan Kipfer and I talk about the lessons we learned from reading the revolutionary Frantz Fanon, author of The Wretched of the Earth and Black Skin, White Masks.
The Anti-Empire Project Episode 51: What is Ecological Economics? With Peter Victor.
I talk to Ecological Economist Peter Victor, author of Managing Without Growth, about the idea of the economy taking place within a biological envelope, what is required for market prices to reflect value, and the pitfalls of the valuation of natural capital.
The Anti-Empire Project Episode 50: Iranian Tanker Arrives in Venezuela – quick reaction
A quick 12 minute reaction as the first Iranian tanker (Fortune) arrives in Venezuela with gasoline to alleviate shortages there. Some notes on the cruelty of the US sanctions regime, on why an oil producing country like Venezuela needs gasoline (for now), and what is likely to happen next.
The Anti-Empire Project Episode 49: Beyond the Green New Deal, with Stan Cox
I talk to Stan Cox about his new book, The Green New Deal and Beyond: Ending the Climate Emergency While We Still Can. We talk about the good aspects of the Green New Deal (especially the New Deal aspects), some of the assumptions that will have to be revised (that good fuels will automatically crowd out bad, that we can grow our way out of the emergency, etc.) and discuss some policies that could actually work.
Civilizations Series Episode 8: Ideas – Scientific Revolution – Enlightenment
We talk about the scientific revolution – Galileo, Brahe, Kepler, Newton, Rousseau, Voltaire, Montesquieu and others; and take a tour of the Enlightenment as well, and the importance of Enlightenment ideas in the revolutions that would soon follow it.
Civilizations Series Episode 7: Religion – Tolerance – Intolerance, Mostly in England
Dave Power and I talk about the rise of Protestantism, focusing on the characters of Martin Luther (including his advice to Philip Landgrave of Hesse), and Henry VIII.
Anti-Empire Project Episode 48: The Goudreau-Silvercorp Coup in Venezuela, Foiled
I talk to Maria Victor after the foiling of the May 3, 2020 terrorist plot against Venezuela, which involved the infiltration of American mercenaries by boat from Colombia. One of the mercenaries, Jean Goudreau of Silvercorp, gave an interview just before the attack where he revealed a signed contract with self-declared president Juan Guaido. We talk about this as the latest in a continuous run of coup attempts against Venezuela for the past twenty years.